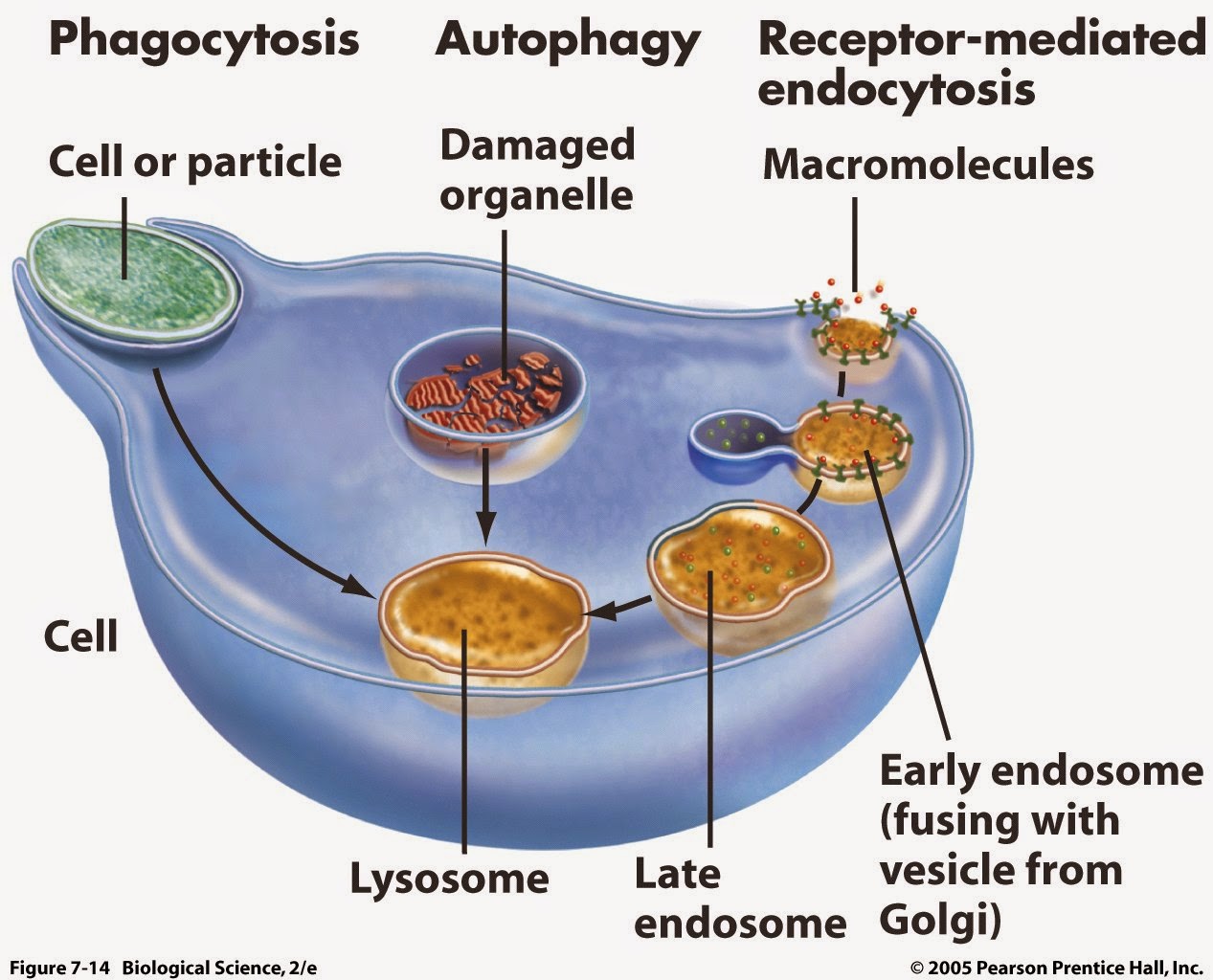
To learn more about how lysosomes can communicate with the rest of the cell to act as recycling centers of cellular waste material in good times and about how lysosomes can act as overly-filled, toxic trash cans in bad times, contributing to cell death and the onset of disease, join us this Wednesday, April 7th for this week’s Marin Science Seminar “Let’s Learn About Lysosomes“ with Gouri Yogalingam, Ph.D. of the BioMarin in Room 207 at Terra Linda High School in San Rafael.
Interview with Dr. Katie Ferris of UC Berkeley
 |
| Monkey Flower |
 |
| Dr. Katie Ferris, UC Berkley |
Why Matter Matters for the Large Hadron Collider
 How does your research on subatomic particles relate to matter on a larger scale? In other words, how do you answer people’s questions about why your research on matter matters?
How does your research on subatomic particles relate to matter on a larger scale? In other words, how do you answer people’s questions about why your research on matter matters?
http://cms.web.cern.ch/news/first-z-bosons-detected-cms-heavy-ion-collisions
 |
| Figure 1: Candidate Z boson decaying to two electrons (two tallest red towers) in a lead-lead heavy ion collision at CMS. The other red and blue towers indicate energy deposits in CMS from other particles produced. |
The Magic of a New Large Hadron Collier
 |
| Large Hadron Collider, Switzerland |
 |
| Higgs Boson |
Interview with Steve Croft, Ph. D. on Black Holes
 |
 |
| Steve Croft, Ph. D. |
Expanding Horizon: How Black Holes Grow
Contrary to popular opinion, black holes do not exist solely to swallow up your socks, keys, and the last scoop of Rocky Road you were saving for a late night snack. Rather, a black hole is an object with such a large mass in such a small volume that nothing, not even light, can escape its gravitational pull. The black hole’s gravitational pull absorbs whatever is in its reach.
For more information, come to the next Marin Science Seminar at Terra Linda High School from 7:30-8:30 p.m. on March 11th, 2015.
Sources:
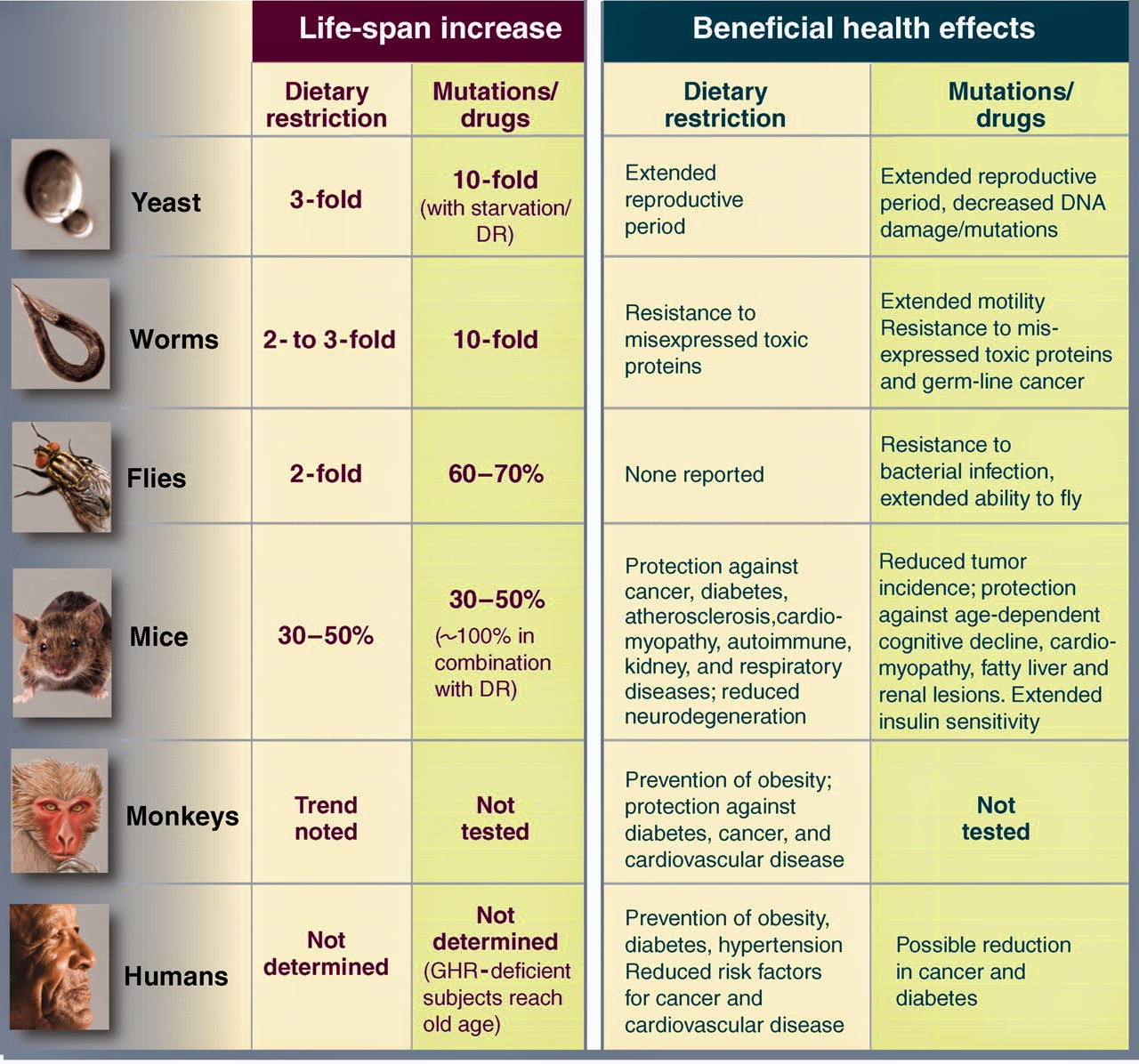
Why Do We Age?
Teaser vid for “Do We Have to Grow Old: The New Science of Aging” Marin Science Seminar
Do We Have to Grow Old? The New Science of Aging
Aging remains one of the most mysterious processes in science. It is also the leading cause of chronic diseases such as cancer and Alzheimer’s disease. Gordon Lithgow studies the basic science of aging at the Buck Institute in Novato. He will talk about what we know about the mechanisms of aging and what scientists are doing to slow aging and eventually eradicate the chronic diseases of late life.
Do We Have to Grow Old? The New Science of Aging Trailer from Marin Science Seminar on Vimeo.
Join us and Learn!
marinscienceseminar.com
Interview with Art Wallace, MD PhD on Big Data and Medical Innovation
In the upcoming Marin Science Seminar, “Big Data and Medical Innovation,” Dr. Art Wallace, Chief of Anesthesia Service at the San Francisco VA Medical Center and a Professor of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Care at UCSF Medical Center, will discuss applications of Big Data in medicine and how Big Data has changed epidemiology, quality improvement, and drug discovery. Read the following interview to learn more about Dr.
Wallace’s thoughts on Big Data and its impact on medical innovation.
 |
| Art Wallace, MD PhD |